1 2 nn in different parts of speech. Complex cases of writing n – nn
1. Suffix -N- is written:
· In adjectives formed from nouns using the suffixes –AN-, -IN-, -YAN-: leather – leather, goose – goose, silver – silver.EXCEPTIONS: wooden, tin, glass.
· In adjectives and participles formed from imperfective verbs that do not have dependent words: forged, loaded, baked, gilded, smoked.EXCEPTIONS:
seen, given, done, desired, cutesy, slow, pecked, sacred, heard, arrogant.
· In adjectives with the prefix NOT-: quicklime, uninvited, uncut, unbleached, unworn. EXCEPTIONS:
unexpected, unforeseen, unheard of, unseen, unexpected, unseen.
· In short forms of passive past participles: sown, filled, set, excited.
· In short adjectives and in adverbs formed from full adjectives with -H-: confused - confused, mad - furiously, gilded - gilded, ruddy - rouge, young - yuna.
· In adjectives related to non-derivatives: crimson, green, blue, ruddy, young, and also in some other adjectives: mutton, single, pork, smart.
2. Suffix -NN- is written:
· In adjectives formed from nouns ending in -H: long, valuable, captivating, picturesque.
· In adjectives with suffixes -ONN-/-ENN-: propaganda, station, cranberry, straw.
· In adjectives formed from perfective verbs, usually with prefixes or dependent words: frozen, mowed, forged, smoked, purchased, dried in the sun. EXCEPTIONS: named brother, imprisoned father, dowry.
· In adjectives formed from verbs ending in -OVAT/EVAT: uprooted, motivated.
· In adjectives formed from nouns ending in -МЯ: nominal, seed, temporary, parietal.
· In short adjectives and adverbs formed from full adjectives with -НН-: inspired, excited, educated(those. literate).
NOTE:
1. In some cases, the spelling of adjectives with -N- or -NN- is determined by the semantics of the word.
wind have:
suffix -YAN- if they define an object powered by wind (windmill);
the suffix -EN- if they define an object containing wind (windy day, windy girl);
suffix -ENN- in all prefixes (windless, leeward, weathered).
Adjectives from the generating stem oil have:
the suffix -YAN- if they define something that is cooked in oil, or something that runs on oil (oil paint, oil pump);
suffix -EN- if they define something that is specially spread with butter (butter pancakes, butter cakes, hence Maslenitsa, this also includes the metaphorical epithet buttered eyes);
suffix -ENH- in participles and adjectives with dependent words (hands oiled with cream, oily sweatshirt).
2. It is necessary to distinguish between the forms of a short adjective and a short participle in the function of a predicate: the girl is brought up - the girl was raised by her grandmother; the woman is educated – the department was founded last year; the group is organized in all matters - the conference is organized by the department.
Questions for control:
Assignments on the topic:
Exercise 1. Form verb forms whose suffixes retain the vowel infinitive.
Depend, fold, knead, stir, deflate, roll out.
Task 2. Explain how the words in pairs differ. Using reference material, explain their spelling.
To decorate - to paint, to be late - to participate, to count - to advise, to manage - to admonish, to confess - to educate, to dance - to hum.
Task 3. Write down, highlighting spellings and grouping words into columns:
1) valid prib. present vr., 2) suffering. prib. present vr., 3) actual. prib. pr. vr., 4) suffer. prib. pr. vr. Explain the spelling of words according to the diagram (see "Reference Material").
creeping, barking, barking, chasing, noticing, noticed, kneaded (in dough) - kneaded (dough), sawing, piercing, struggling, developed, cherished, pumped out (oil from a barrel) - pumped out (from a barrel barrel), provided, hung (in the gallery of paintings), hung (a kilogram of sugar), traveled, well-trodden, fanned, provided, healing, adhesive, glued, enduring, loving, dispelled, traveled, dependent, breathing, watering.
Task 4. Insert the missing letters and justify your choice.
A job corrected by someone, a load dropped, paths cleared; the building is about to be built...but; alarmed...by unpleasant news, crowned with laurels, scattered rays, an unnoticed friend, tangled hare tracks, leaf-strewn alleys of a coastal park, offended by someone... that girl, wasted time; the snow melted unexpectedly, without offending anyone.
Task 5. Insert the missing letters.
Nurtured, kneaded (dough), dropped, noticed, engaged, significant, studied..my, cherished, chalked. ..unpreserved, underweight (grain), underweight (curtains), independent, hated...my, offended...my, justified...my, celebrated, transferred..., shot... (deer), shot... (gun), shot... (traitors), scattered..., dispersed, heard... , creeping, dragging, dragging, lost, crowned.
Task 6. Explain the difference in spelling of words in paired phrases.
The woman is smart and educated. - The commission was formed the other day.
The children were inattentive and absent-minded. - The troops were scattered throughout the forest. He says depressed. “The uprising was suppressed.” The decision was hasty and ill-considered. - The decision has not been thought through by anyone. Sauerkraut is cabbage fermented for the winter. Unmown meadow. - Mowed meadow. Come to a dinner party. - Uninvited guests. sworn brother. - Named after you. Windy day. - Calm day.
Remember:uninvited n oh, name n oh, unseen nn oh, unheard of nn oh, unexpectedly nn oh bad luck nn O
Task 7. Replace the dots with the missing letters. Explain why in some cases we write N,in others - NN.
Bee...honey, wheat...porridge, with condensed...milk, oil...stain; painting, rice:... with oil paints; a clay vase, a wooden building, located in a guest...ice, noticeable shortcomings, a rye...field sown, a meadow not yet mown, some sort of ...things hanging...in the wardrobe...about the target...harvest, the girl is very educated...and, far away...draw a broken line, silver and gold... jewelry, a wounded man, a seriously wounded fighter, at dawn.
Spelling N and NN in nouns
In derived nouns n
or nn
written depending on the morphemes with which nouns are formed, or in accordance with the stem from which they are derived. 1. nn is written:
1) if the root of the word ends in n and the suffix begins with n: elder-nick (elderberry), druzhin-nick (druzhina), malin-nick (raspberry), swindler-nick (moshna), aspen-nick (aspen), rowan-nick (rowan); besdorn-nits-a (dowry), besson-nits-a (sleep), zvon-nits-a (ringing), log-nits-a (log);
2) if the noun is formed from an adjective with nn, or from a participle: soreness (painful), agitation (excited), hryvnia (kryvnia), power of attorney (confided), cutesy (prissy), spoiled (spoiled), izbn-ik (chosen), exiled (expelled), konn-itsa (horse), koren-ik (indigenous), larch-itsa (deciduous), accident (accidental), education (educated), obshchestven-ik (public), organization ( organized), plenn-ik (captive), possan-ik (sent), privileged-ist (privileged), proizvodstven-ik (productive), millet-ik (millet), crafts-ik (craft), sotsanny-ik (related ), sacred-ik (sacred), seminal-ik (seminal), sov-ik (own), sovrem-ik (modern), coherence (coordinated), nebula (foggy).
2. N written in words: bagryan-itsa (crimson), varen-ik (boiled), windy-ost, windy-ik, windy-itsa (windy), gostin-itsa (living room), drovyan-ik (wood-burning), konoplyan-ik (hemp) , kopchen-ost (smoked), kostyan-ika (bone), maslen-itsa (oily), wiser-ost (sophisticated), ovsyan-itsa (oatmeal), peat-ik (peaty), smyshlen-ost (smart) and etc., as well as in the words alder-nik, omshan-ik.
Spelling Н and НН in suffixes of denominal adjectives (formed from the name of a noun)
1. Nn is written:1) for adjectives formed from nouns using suffixes -enn-, -onn-: artificial, cranberry, straw, operating, session, station and etc.; This also includes adjectives formed from nouns ending in mya (time, flame, etc.): temporary, fiery, seed, nominal, tribal etc.
In an adjective windy one is written n , since it is formed not from the noun wind, but from the verb wind using a suffix -n- , which does not contradict the spelling rule n in verbal adjectives: weathered, weathered, windswept- formed from verbs;
2) for adjectives formed from adjectives using a suffix -enn-, indicating a large measure of a sign: tall, hefty, wide and etc;
3) for adjectives formed from nouns with base on n(second -n- adjective suffix): long (length), true (true), millionth (million), ancient (antique), canvas (canvas) and etc.
Adjectives like mutton, carp, seal are written with one n , since they are formed from nouns with a stem in n by adding a suffix -j- .
Words spicy, rosy, youthful written with one n (non-derivative adjectives); in words derived from them, one n is also written: spice, ruddy, blush, youth(But: youth, since this word is formed from the combination young naturalist).
2. N is written on adjectives formed from nouns using suffixes -in-, -an-, -yang- : pigeon(pigeon), goose(goose), chicken, eagle, swan, leather(leather), sandy(sand), cereous(wax), linen(canvas), silver, wood-burning and etc.
Exceptions: glass, tin, wood.
It is necessary to distinguish between adjectives, the spelling of which depends on their meaning:
A) windy- “accompanied by the wind, with the wind” (windy weather), “frivolous” - transl. (fickle girl, youth); wind- “powered by the force of the wind” (wind engine, pump, mill); in combination chickenpox the adjective is written with a suffix -yan- , cf.: chickenpox- decomposition;
b) buttery- “soaked in oil, lubricated, stained with oil” ( butter pancakes, porridge, hands), trans. ( oily eyes, oily voice, also: Shrovetide week - Maslenitsa); oil- “for oil, from oil, in oil” ( oil cookies, oil paint, oil engine, pump and so on.); compare: oil bottle(“intended for oil”) and buttery bottle(“stained with oil”);
V) silver- “subjected to silvering, covered with silver” (silver spoon); silver- “made of silver” (silver spoon);
G) salty- “containing salt” (salted fish); salt- “consisting of salt” ( salt mine, salt pillar). In combination salt acid is written as a suffix on the adjective -yan- .
Spelling N and NN in verbal adjectives and participles
Full forms
Written with nn suffixes of full forms of passive past participles: -nn- And -yonn- (-enn- ). Adjectives correlative to them in form are written in some cases also with nn in a suffix, in others - with one n .
1. Written with nn participles and adjectives -ovanny, -evanny, -evanny(formed from verbs in -ow, -eat), For example: pampered, uprooted, lined, painted, organized; uprooted, spoiled, painted over, lined, reorganized.
2. Also written with nn communion not on -ovated(-evanny, – evanny) verbs perfect form and correlative adjectives; the vast majority of such verbs contain a prefix.
a) Examples of forms formed from prefixed verbs: bleached, washed, knitted, fried, written on, dyed, peeled, scolded, dyed, counted, unraveled, made.
b) A list of forms of native verbs without prefixes, as well as some verbs in which the prefix can only be distinguished etymologically: abandoned, given, finished, bought, deprived, captured, forgiven, abandoned, decided, captured, revealed; met, started, offended, acquired, obliged, visited, supplied.
Forms are also written according to this rule. two-species(having the meaning of both perfective and imperfective forms) verbs to marry, bequeath, promise, execute, give birth: married, bequeathed, promised, executed, born.
Exceptions. Are written with one n adjectives correlative with participial forms in the following stable combinations: finished man, named brother, named sister, imprisoned father, imprisoned mother, Forgiveness Sunday .
3. Participles are not on -ovated(-evanny, -evanny) verbs imperfect form(they are formed only from prefixless verbs) and the adjectives correlative with them are written differently: participles with nn , adjectives – with one n , For example: carts loaded with firewood, fish fried in oil, an oil painting, hair cut by a barber And short-cropped hair, green-painted benches, a floor that has not been swept for a long time, walls that have not yet been whitewashed, money that has been counted more than once, an offer made many times; But: loaded barge, fried fish, painted beauty, cut hair, painted benches, swept floor, whitewashed walls, a few minutes, feigned indifference; similarly knitted And knitted, ironed And ironed, woven And braided, brushed And cleaned; also written: chewed And chewed, pecked And pecking, forged And forged.
According to this rule, forms of two-type verbs are written concuss, baptize And injure. Wed: a shell-shocked soldier, a seriously wounded soldier, a soldier wounded in the leg, a newly baptized baby, But: shell-shocked commander, wounded soldier, baptized child.
As can be seen from the examples, the participle is recognized by the presence of dependent words. There are, however, rare cases when the dependent word is not a sign of the participle. For example, you should write: his mustache is clearly dyed(obviously artificial, where is the word obviously used with an adjective); the walls, previously whitewashed, are now covered with green paint(walls that used to be white).
In words with the prefix not-, in compound words and in some combinations? repetitions, the forms of participles and adjectives are written in the same way as in a separate (without a prefix and not as part of a compound word or repetition combination) use .
Examples:
1. Words with a prefix Not- :
Written with nn : uneducated, unlined, untested, unfinished, unbought, unforgiven ;
Written with n : unbleached, unironed, uninvited, unforged, unfed, unpainted, unmeasured, unpaved, unplowed, uninvited, uncounted.
2. Difficult words:
Written with nn : highly qualified, fully stamped, acquired, freshly painted, purposeful, born blind, insane;
Written with n : plain dyed, homespun, finely crushed, impostor, seriously wounded, whole-cut .
3. Repeat combinations with a prefix re- in the second part, having an intensifying meaning. In them, the second part is written in the same way as the first (with nn or n ), For example:
Written with nn : mortgaged-remortgaged, resolved-resolved ;
Written with n : patched-re-patched, washed-re-washed, mended-re-fixed, read-re-read, darned-re-darned.
Exceptions. Written with nn instead of n :
a) adjectives desired, awaited and (as part of stable combinations) has it been seen before?; Is it unheard of? They are formed from imperfect verbs wish, wait And see, hear .
Special cases: adjectives put on flooded sea; they are formed from imperfect prefix verbs put on, pour out, i.e. from verbs with a suffix - va- , which do not naturally form passive past participles;
b) adjectives with a prefix not-: unknown, unseen, unforeseen, unwanted, unexpected, unexpected, unexpected, unheard of, unexpected and (as part of a stable combination) watchful eye;
c) compound adjectives long-awaited, home-grown and (as part of a proper name) Andrew the First-Called.
The second parts of these prefixed and compound adjectives also correspond to imperfective verbs.
Short formsShort forms of passive past participles are written with one n , For example: read, read, read, read; read, read, read, read; tagged, tagged, tagged, tagged; marked, marked, marked, marked. Neuter forms are also written in impersonal use, for example: smoked, polluted, driven, walked, driven-crossed, walked-crossed .
Short forms (except for the masculine form) adjectives with a qualitative meaning, coinciding in form with the passive participles of the past tense of perfective verbs, written with nn , For example: brought up, brought up, brought up(from adjective well-mannered‘discovering the results of good education’); spoiled, spoiled, spoiled(from adjective spoiled‘accustomed to fulfilling one’s whims’); sublime, sublime, sublime(from adjective exalted‘full of high content’). Such adjectives have comparative forms: more educated, more spoiled, more elevated.
Compare the following examples in pairs with short forms of participles and adjectives: She was raised by a distant relative . – She has good manners and is well-mannered. She is spoiled with good conditions – She is capricious and spoiled.
Short forms of adjectives na-ny are written with one n , if these adjectives require dependent words and do not have a comparative form. Examples: attached to someone‘attached’ – She is very attached to him; full of something‘full, imbued’ – The soul is filled with sadness; heard about something‘well-informed’ – We've heard a lot about his tricks.
Some adjectives have different short forms with different meanings. For example, different spellings of short forms of the word devotee: She is kind and loyal And She's dedicated. In the first example devoted- same adjective as educated, spoiled, sublime, it has a comparative degree more faithful; in the second - the same as attached, fulfilled, heard(requires dependent words: to anyone, anything).
Short forms of adjectives, expressing different emotional states, can be written with n or with nn depending on the conveyed shades of meaning. For example: She's excited(she feels nervous) – Her speech is excited(her speech reveals, expresses excitement). In the first case, it is also possible to write excited(which would emphasize that her appearance expresses excitement), and in the second case the writing excited impossible (since speech cannot ‘experience excitement’).
In difficult cases of distinguishing such short forms, one should refer to the academic “Russian Spelling Dictionary”.
Short forms of complex adjectives, the second parts of which coincide with the participles on -ny, written with n or nn depending on the value. Adjectives expressing characteristics that can be manifested to a greater or lesser extent, i.e. forming comparative forms, have short forms (except for the masculine form) with nn ; adjectives that do not allow comparative forms in meaning have short forms with one n , For example:
well-mannered, -no, -nny; landscaped, -no, -nny; self-confident, -no, -nny; purposeful, -no, -nny; purposeful, -no, -nny(there are comparative forms more well-mannered, more comfortable, more self-confident, more purposeful, more purposeful);
interconnected, -but, -us; interdependent, -but, -us; generally recognized, -but, -us; contraindicated, -but, -we(no forms of comparative degree).
Short forms of adjectives with a qualitative meaning, the full forms of which are conveyed in writing with one n , are written in the same way as complete ones. For example: done, done, done(from made‘unnatural, forced’); prostitute, confused, prostitutes(from confused‘illogical, confusing’); scientist, scientist, scientists(from scientist‘knowing something thoroughly’). Comparative forms are also written ( more elaborate, more confused, more learned) and adverbs -O(done, confused, learned).
Such adjectives are few in number; the vast majority of adjectives correlative with participles -ny have no qualitative significance; these are boiled, boiled, soaked, dried, chiseled and so on.
SPELLING N-NN IN ADVERB SUFFIXES
Adverbs on -O , formed from adjectives and passive participles, are written with double n or one n - depending on how the corresponding adjective or participle is written.
For example:
Written with nn : unexpected, unheard of(from unexpected, unheard of), excitedly, excitement(excited), confident;
Written with n : confusing(talks confusedly), confusion, confusion(from confused), learned(very learnedly expressed),windy(It's windy outside today).
Н-НН in adverbs, adjectives and participles, full and short
1. With one letter n are written:
1. Adjectives with a non-derivative base: red, young, blue. There is no suffix in such adjectives. Letter n is part of the root.
2. Denominate adjectives with suffix -n: winter n th(from: winter), years n th(from: summer).
3. Denominate adjectives with suffixes -an, -yan: sandy, silver (adj. meaning “name of material, substance”), and -in: mouse, passerine (adj. meaning “accessories”).
Exception:
wooden, tin, glass write with two letters nn.
4. Verbal adjectives, if there is no prefix and explanatory word: heat fresh meat .
Exception:
Write with two letters nn words from the list:
given, arrogant, abandoned, desired, bought, seen, made, cutesied, captivated, deprived, sacred, read, desperate, minted, cursed, unheard of, unseen, unexpected, unforeseen
Do not confuse:
The list of exceptions does not include words uninvited, uninvited, named, which are consistent with the data above. Write them according to the rule: unsolicited advice, uninvited guest,sworn brother.
5. Short adjectives in the masculine singular form: advice is valuable - (m.r.), as well as short adjectives in all other forms if they are formed from full adjectives with one letter n: red girl (from the full form with one letter n: red), the sun is red, the girls are red.
6. Adverbs on -O And -e formed from adjectives with one letter n: windy, neat.
2. With two letters nn are written:
1. Denominate adjectives with suffix -n, if the root of the noun ends in a letter n:autumn, spring, sleepy.
2. Denominate adjectives with the suffixes -enn, -onn: letter, portion.
Exception:
flighty man, windmill, chicken pox, But windless day,leeward side.
3. Verbal adjectives with suffix -nn : korcheva nn y plot, Brakova nnth thing.
Figure out how the word is formed: defective ← reject + nn .
Suffix -nn write in verbal adjectives formed from a generating stem with suffixes: - Eve//-ova,-Eve: uprooted←uproot, formed←form.
It’s easier to remember this way: adjectives on Eve+nn + th,ova +nn +y, eva +nn+ y.
4. Adjectives-exceptions from clauses:
1.3.Exception: wood, tin, glass write with two letters - nn .
1.4.Exception: the, swaggering, abandoned, desired, bought, seen, made, cutesy, captive, deprived, sacred, read, desperate, embossed, damned, unheard of, unprecedented, inadvertent, unexpected.
5. Passive past participles, if there are prefixes or explanatory words: a written essay, mittens knitted (by whom?) by grandmother, as well as participles and verbal adjectives formed from perfective verbs without prefixes: bought, abandoned, given (the latter are included in the list words to remember in paragraph 5 along with other examples).
6. Short adjectives formed from the full form with two letters nn(except for the form m.r. singular, in which there is always one letter n): night without moon n a, adviсe prices.
7. Adverbs on -O And -e, formed from adjectives with two letters nn: sincerely, thoughtfully, calmly.
So, in order not to make mistakes in the exam, you need to know all the points. Be sure to include examples, because examples are samples that help you act by analogy.
Do not forget about the exceptions in paragraphs: 1.3., 1.4., 2.2.
Attention:
To expand your language experience, you can refer to the section.
This is a constructor dictionary. Set the parameters you are interested in and get the necessary lists of words.
It is now useful for you to turn to the Correct Dictionary, as well as to the Grammar Dictionary. Don’t forget, you can connect the following parameters: “New”, “Easy”, “Difficult”, “Important”. You can add or, on the contrary, exclude words for grades 5-8. Create your own dictionary configuration on the topic tasks 14.
The topic of the Russian language “Spelling “n” and “nn” in adjectives” is familiar to every schoolchild. However, after graduating from a general education institution, many people begin to forget the simplest rules and make a large number of mistakes when creating any text. In this regard, we decided to remind you of the cases in which the suffixes “n” and “nn” are written in adjectives. You will also be presented with some exceptions to the current rules. They should be remembered.
Definition of part of speech
They call the nominative, which denotes a non-procedural attribute of an object, and also acts in a sentence as a definition or a nominal part of the predicate and answers the following questions: “which?”, “which?”, “which?”, and also “whose?” and what?".
general information
“Spelling “n” and “nn” in adjectives” is a very important topic in the Russian language. After all, without knowledge of such simple rules, it is quite difficult to compose a literate text or even a letter.
It should be especially noted that adjectives can be formed both from nouns and from verbs. Knowing these basics will allow you to better understand how many “n”s you need to write in a given case.
Spelling "n" and "nn" in adjectives derived from nouns
So, let's figure out together in what cases you should use -nn-:

Which adjectives that come from nouns are spelled "n"?
Now you know in what cases the suffixes -NN- are written in adjectives (-ONN-, -ENN-, etc.) if they are formed from nouns. However, this is not enough to compose the text correctly. In this regard, it is necessary to consider the spelling rules of the suffixes -in-, -yan- and -an-:
- In adjectives that are derived from nouns using the above suffixes, only 1 letter “n” is always written. Let's give an example: leather (leather), sparrow (sparrow), clay (clay), pigeon (dove), wax (wax), crane (crane), wood (firewood), nightingale (nightingale), etc. However, all rules have your exceptions. In this case, the words are “glass”, “wooden” and “tin”. They contain 2 letters “nn”, and you should definitely remember them.
- In adjectives that are formed without using any suffixes. Let's give an example: green (green). You also need to remember the following words: spicy, rosy, porky, young and united.

How many "n"s are there in adjective names that come from adjectives?
2 letters “n” are written if adjective names are formed from adjectives by adding the suffix -enn-, which indicates a greater measure of any attribute. Let's give an example: hefty, tall or wide.
Important notes regarding the rules described
The spelling of “n” and “nn” in adjectives also has the following features:

Spelling "nn" in adjectives and participles derived from verbs
So, 2 letters “n” should be written if:
- Adjectives are formed from verbs with prefixes. Moreover, the prefix “non” almost never affects the spelling of “n” or “nn”. Thus, in an adjective with you should not write the same number of letters “n” as in an adjective without this prefix. Let's give an example: (tied, beveled, built).
- If there are suffixes such as -eva- or -ova-. Let's give an example: an organized excursion, an uprooted forest, etc.). The following words are exceptions: chewed And forged. In this case, ov- and ev- are part of the root, and are not suffixes.
- If the sentence contains any dependent word (for example, wicker).
- If the adjective is formed from a verb that has a perfect form (for example, solved). The exception is the word “wounded”.
Spelling "n" in adjectives derived from verbs
One letter "n" is written in adjectives that are derived from verbs without the use of prefixes. Let's give an example: uncut, knitted. The exceptions are the following words: sacred, slow, unprecedented, unexpected, desired, unheard, unexpected and unexpected.

Letters "n", "nn" in short adjectives
In addition to the full names of adjectives, the Russian language also has short forms. To understand how “n” and “nn” are written in short adjectives, you should remember the rules about full ones. After all, they are the same for both forms.
Here's an example:

Important notes on the material covered
To finally understand how to write adjectives (with “n” or “nn”), you need to consider the following features:
1. Usually the suffixes -yan- and -an- give the meaning “intended for something” or “made of a certain material.” For example: wood, clothes; sandy, clay.
2. To compose a text correctly, you should distinguish between adjectives whose spelling is related to their meaning.
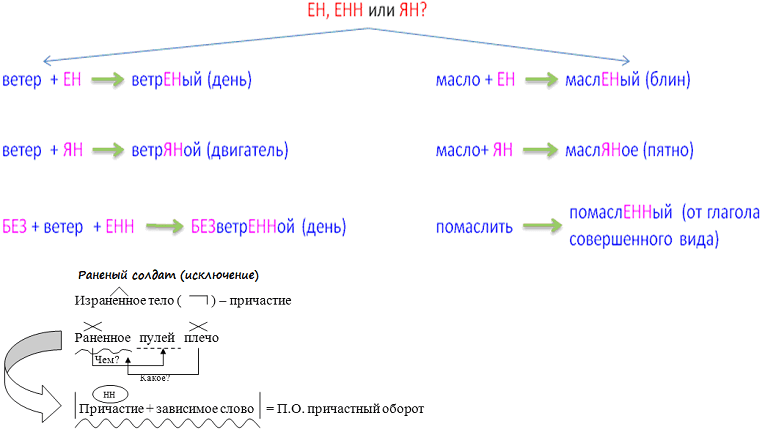
Windy, that is, “with the wind” (windy weather). Wind powered, that is, “powered by the power of the wind” (wind pump). In the phrase “chicken pox” the adjective name is written with 1 letter “n”. This is due to the fact that this word comes from “chickenpox”.
Buttered, that is, “soaked in oil” (butter porridge). Oily, that is, “flattering” (oily voice). Butter, that is, “diluted in butter” (butter cookies).

Silver, that is, “subjected to silvering” (silver device). Silver, that is, “made of silver” (silver bottle).
Salty, that is, “containing salt” (salted fish). Solyanoy, that is, “consisting of salt” (salt column).
Spelling –Н- and –НН- in suffixes of various parts of speech
This activity requires knowledge of how words are formed!
Clue. You can find information about them in task B1.
Rule.
Depending on the part of speech, the rule is divided into three parts.
Full adjectives and participles.
Remember! Both parts of speech in the initial form answer the question: Which?
Remember!
| unexpectedlyNNth
slowerNNth countryNNth sacredNNth wowNNth checkNNth wishedNNth okayaNNth affairsNNth invisibleNNth unheard ofNNy unexpectedlyNNth unexpectedlyNNth bad luckNNy jamNNth |
rdyaNth
straightNth greenNth sviNOuch barNth siNth blushingNth crimsonNth YuNth smarterNth nameNy (brother) plantingNy (father) |
Distinguish!
Short adjectives and participles.
To cope with this part of the rule, you need to know the signs of each part of speech.

Nouns and adverbs.
There are as many N written in adverbs as in the words from which they were formed:
looked beshe?o - beshe?yy (see part No. 1 of the rule: formed from the verb to enrage the imperfect form, without the prefix and suffixes -OVA/-EVA = besheNy = besheNo)
Remember!
Before you apply a rule, see if this word is an exception! These include:
MosheNNik harderNIR
tribeNNik pridaNoh
putNNIR
YesNNIR
lawlessnessNNitza
Algorithm of actions.
1. Determine what part of speech are the words in which –Н- or –НН- are missing. This is necessary in order to know which part of the rule to use.
2. Remember if this word is an exception.
3. Think about what word the words being analyzed are formed from.
4. Determine the spelling according to the rule.
Analysis of the task.
Which answer option correctly indicates all the numbers in whose place NN is written?
His manners were not simple, but rather sophisticated. In the labyrinth of crooked, narrow and feeble streets, people were always sneaking around. The drivers argued with the loaders that the car was underloaded (3).
1) 1,2 2) 1,3 3) 1,2,3 4) 1
Manners are (what?) sophistication(1). This is a short adjective as it can be replaced with the full form exquisite. Determine the spelling of the full form: exquisite derived from the verb find, in which there is a prefix from-. Thus, we write two NNs in both full and short form.
Weak(2)th (which?) streets. This is a full adjective formed from an imperfective verb pave. The prefix ne- does not affect the spelling, there are no suffixes –OVA/-EVA, and there are no dependent words either. We write one N.
The machine is underloaded (3) (what has been done?). This is a short participle because it can be replaced with a verb underloaded. In short participles one N is written.
Thus, the correct option is answer No. 4.
Practice.
1. Which answer option correctly indicates all the numbers in whose place NN is written?
The house stood somewhat away from the forest; its walls here and there were renovated (1) with fresh wood, the windows were painted (2) white, a small porch on the side, decorated (3) with carvings, still smelled of resin.
